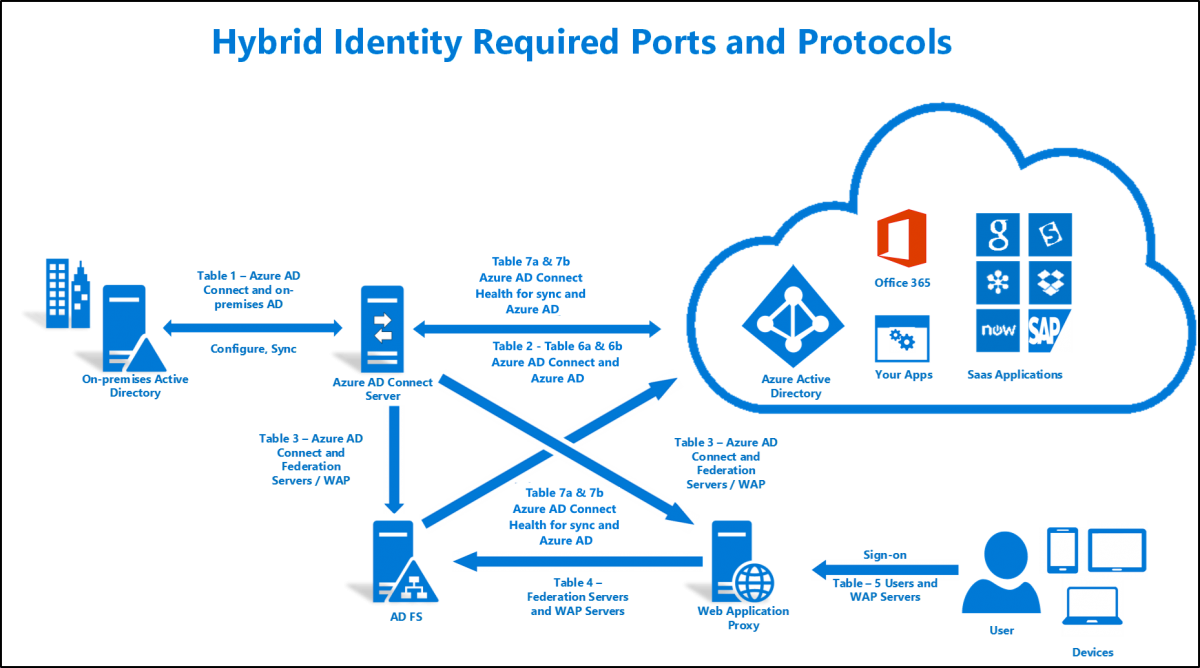
SNMP The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) enables remote query and remote configuration of just about anything on a network. Assuming all your computers, switches, routers, and so on are SNMPcapable, you can use programs to query the network for an unimaginable amount of data. SNMP is a popular tool to check on your network, but you’ll need to take the CompTIA Network+ exam to see SNMP in action. SMB The Server Message Block (SMB) protocol isn’t even an application but rather proof of the power of Microsoft. SMBs date…
Ports identify how a communication process occurs. Ports are special addresses that allow communication between hosts. A port number is added from the origi- nator, indicating which port to communicate with on a server. If a server has a port defined and available for use, it will send back a message accepting the request. If theport isn’t valid, the server will refuse the connection. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) has defined a list of ports called well-known ports. A port address or number is nothing more than a bit…
Organizations in all industries-particularly financial services, retail, and communications-are increasingly dependent upon IT and a highly available network to meet their business objectives. In particular, the advent of online business transactions has made the network a critical business component that is expected to function properly with little or no downtime. As customer expectations and demands rise, network operations teams are focusing on IT service-quality improvement and achieving higher levels of availability by re-examining processes and procedures-particularly in the area of change management-because changes to the network are often a source…

Intermediate distribution frame hort for intermediate distribution frame, a cable rack that interconnects and manages the telecommunications wiring between an MDF and workstation devices. Cables entering a building run through a centralized MDF, then each individual IDF and then on to specific workstations. For example, an enterprise that encompasses a building with several floors may have one MDF on the first floor and one IDF on each of the floors that is connected to the MDF. Main distribution frame Short for main distribution frame, a cable rack that interconnects and…

Electrical safety Shielding refers to the process of preventing electronic emissions from your computer systems from being used to gather intelligence and preventing outside electronic emissions from disrupting your information-processing abilities. In a fixed facility, such as a computer center, surrounding the computer room with a Faraday cage can provide electronic shielding. A Faraday cage usually consists of an electrically conductive wire mesh or other conductor woven into a “cage” that surrounds a room. The conductor is then grounded. Because of this cage, few electromagnetic signals can either enter or…

Security policies Networks and computers may be monitored and usage logged. Logs are kept secure and are only available to personnel authorized by the Director of Information Services and will only be kept as long as necessary in line with current data protection guidelines. Edinburgh Napier University’s networks and computer may be monitored and logged for all lawful purposes including: – Ensuring use is authorized Management of systems Protecting against unauthorized access Verifying security procedures System and operational security Compliance with Edinburgh Napier University policies and regulations Detection and prevention…

Ethernets – 10Base2: 10Base2 is defined as part of the IEEE 802.3a standard. The specifications of 10Base2 are: Characteristic Description Speed: 10Mbps Total Segment Length 185 meters Cable Type RG-58 Coaxial Cable Connector Bayonet Neill Concelman (BNC) Transmission Method Baseband It is prescribed that of each segment one of the physical end is grounded. The network permits a maximum of five segments out of which only three are allowed to be populated with an upper limit of 30 nodes. It is also required that a distance .5 meters be observed…

There are many wireless networking specifications that exist under the umbrella, 802.11. These standards though implemented in the same way have different characteristics in terms of speed, transmission ranges and others. The main standards to be considered are: – IEEE 802.11: This is the initial wireless standard. Two variations of the standard were implemented. In terms of transmission speeds and the radio frequency, the systems were identical, the difference was in the way data traveled through the RF media. FHSS (Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum) was used by one and DSSS…

Encapsulation/de-encapsulation While the data travels down the layers, headers are added which is known as encapsulation and removed as it travels down which is known as decapsulation. The figure given below illustrates the processes. Figure 71: Encapsulation and Decapsulation As the data travels down the decapsulation is done by the corresponding layer, which had added the information. With every movement of the information, it is sorted and arranged in logical groups of bits. A different term is used to define the process at every layer. The terms are: Layer Name …

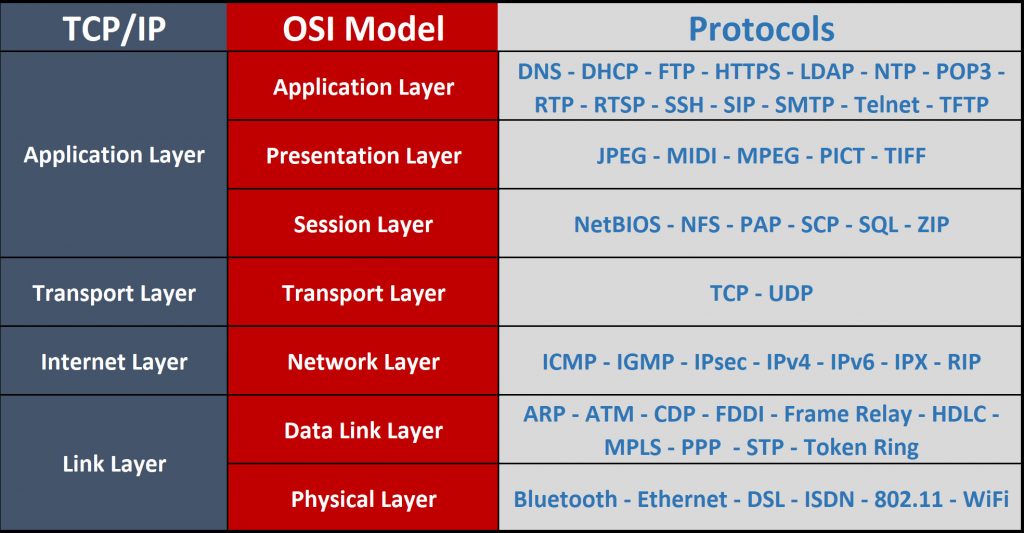
The OSI model consolidates network communications into seven simplified layers. So what are the seven layers? Below, I list them in the order they occur as data gets processed from the sending side of a network communication. The seven layers are: Application Presentation Session Transport Network Data link Physical Application (Layer 7) When a program needs to send a network communication, it first interacts with the application layer. In the OSI context, “application” doesn’t mean Excel, Word, or their ilk. Instead, Layer 7 is the protocol a program like Outlook…











Recent Comments