
Packet/network analyzer The term packet sniffer also refers to protocol analyzer or packet analyzer. Packet sniffers are used to monitor various packets that travel through the network. They run either on computers or they require dedicated hardware devices. There are various packet sniffers available in the market for example Wireshark, HP Open view etc. Figure 52: Wireshark This is the working snapshot of wire sharp packet analyzer. It captures the packets leaving or entering the interface which we want to monitor and displays the output for testing, monitoring etc. Interface…

Wireless Networks can be incorporated for a variety of networks in terms of shapes and sizes. Wireless Networks enable forming connection by using radio waves and not wires. Computers on wireless transceivers (transmitters and receivers) which are known as Access Point (AP) can move around in a premises and do need to be wired for use. Convenience, security and speed are some of the factors that have led to the development of these networks. Before we can understand how to implement a wireless network, it is important to understand wireless…

Virtualization Virtualization is the current rage due to the cost-savings and performance it provides. Virtualization can be implemented through open source solutions (such as Xen and VirtualBox) as well as proprietary solutions (such as VMware), allowing you to take a single physical device and make it appear to users as if it is a number of stand-alone entities. Virtual Servers Just as workstations can be virtualized, so can servers: A single server can host multiple logical machines. Using only one server to does the functions of many, the cost-savings that…

VoIP Long-distance calls are expensive, in part because it is costly to maintain phone lines and employ technicians to keep those phones ringing. Voice over IP (VoIP) provides a cheaper alternative for phone service. VoIP technology enables regular voice conversations to occur by traveling through IP packets and via the Internet. VoIP avoids the high cost of regular phone calls by using the existing infrastructure of the Internet. No monthly bills or expensive long distance charges are required. But how does it work? Like every other type of network communication,…
Loopback interface You can specify a software-only interface called a loopback interface to emulate an interface. Loopback interfaces are supported on all platforms. A loopback interface is a virtual interface that is always up and allows Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and remote source-route bridging (RSRB) sessions to stay up even if the outbound interface is down. You can use the loopback interface as the termination address for BGP sessions, for RSRB connections, or to establish a Telnet session from the device’s console to its auxiliary port when all other interfaces…
IPv6 EUI-64 One of IPv6’s key benefits over IPv4 is its capability for automatic interface addressing. By implementing the IEEE’s 64-bit Extended Unique Identifier (EUI-64) format, a host can automatically assign itself a unique 64-bit IPv6 interface identifier without the need for manual configuration or DHCP. This is accomplished on Ethernet interfaces by referencing the already unique 48-bit MAC address, and reformatting that value to match the EUI-64 specification. RFC 2373 dictates the conversion process, which can be described as having two steps. The first step is to convert the…

Multiple functions like easy communication, sharing of hardware, sharing of data and applications, easy storage and quick retrieval of data are expected from a network. The question in front of businesses these days is not whether to have a network or not but rather which form of network to choose. Networks are categorized depending on the number of locations that they span. The options available are: LAN’s WAN’s MAN’s PAN’s LAN: The full form of LAN is Local Area Network. This type of network caters to only a single location….

A network is a group of connected computers and devices. For the purposes of networking the number of devices and computers is immaterial. The basic objective behind networking is ease of communication and sharing of data and resources. Networking allows easy communication, sharing of hardware, sharing of data and applications, easy storage and quick retrieval of data. The meaning of the word ‘topology’ is the layout of a network. The topology influences the decision regarding what type of networking method, media types and network devices are to be used. Broadly…
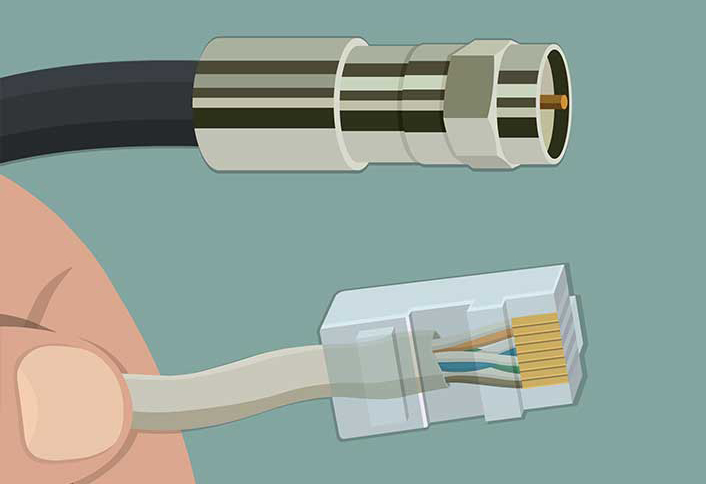
Copper connectors All forms of network media need to be physically attached to the networked devices in some way. Media connectors provide the interface between the cables and the devices to which they attach (similar to the way an electrical cord connects a television and an electrical outlet). RJ Connectors: The RJ-45 is the most commonly used connector in the modern networks. These are quite similar to the RJ-11 connectors used in telephone connections. The RJ-11 connector supports only six wires whereas RJ-45 connector supports eight wires. The figure given…

Fiber Early fiber optic transmission systems put information onto strands of glass through simple pulses of light. A light was flashed on and off to represent the “ones” and “zeros” of digital information. The actual light could be of almost any wavelength (also known as color or frequency) from roughly 670nm to 1550nm. During the 1980s, fiber optic data communications modems used low-cost LEDs to put near-infrared pulses onto low-cost fiber. As the need for information increased, the need for bandwidth also increased. Early SONET systems used 1310nm lasers to…











Recent Comments